Learning Outcomes
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
i. Define and explain the concept of electron configuration and its significance in classifying elements.
ii. Identify and differentiate between groups and periods in the periodic table, recognizing their role in organizing elements.
iii. Classify elements into groups and periods based on the configuration of their outermost electrons, known as valence electrons.
iv. Analyze how electron configuration influences the placement of elements in the periodic table and their position within groups and periods.
v. Apply the knowledge of electron configuration to predict and explain the chemical properties of elements.
Introduction
The intricate world of atoms holds a remarkable order, a pattern that governs their behavior and properties. This order, deeply intertwined with the arrangement of electrons, provides a basis for classifying elements and understanding their chemical characteristics.
i. Electron Configuration: A Map of Electron Distribution
Electron configuration, a fundamental concept in atomic structure, represents the distribution of electrons in an atom's orbitals. It provides a blueprint for understanding how electrons are arranged within an atom, offering insights into their behavior and energy levels.
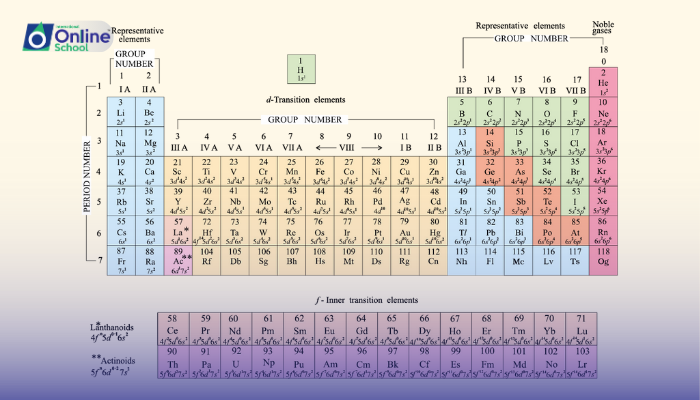
ii. Groups and Periods: A Framework for Classification
The periodic table, a cornerstone of chemistry, serves as a comprehensive arrangement of elements, organized into groups and periods. Groups, the vertical columns, represent elements with similar outer electron configurations, known as valence electrons. Periods, the horizontal rows, represent elements with increasing atomic numbers.
iii. Electron Configuration and Element Classification
The electron configuration of an element dictates its position within the periodic table:
Groups: Elements within a group share the same number of valence electrons, resulting in similar chemical properties.
Periods: Elements within a period have increasing atomic numbers, corresponding to the addition of electrons to the same energy level.
iv. Electron Configuration and Chemical Properties
Electron configuration plays a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of elements:
Valence Electrons and Bonding: Valence electrons, the outermost electrons, are primarily responsible for an element's chemical bonding behavior.
Reactivity: Reactivity of elements is often related to their electron configuration, with elements sharing similar electron configurations exhibiting similar reactivity patterns.
Periodic Trends: The periodic table serves as a powerful tool for predicting and explaining trends in chemical properties based on electron configuration.
The classification of elements based on electron configuration provides a deeper understanding of the periodic table and its organization. By delving into the concept of electron configuration, we gain valuable insights into the chemical properties, bonding behavior, and periodic trends of elements, enabling us to navigate the fascinating world of chemistry with greater clarity and comprehension.